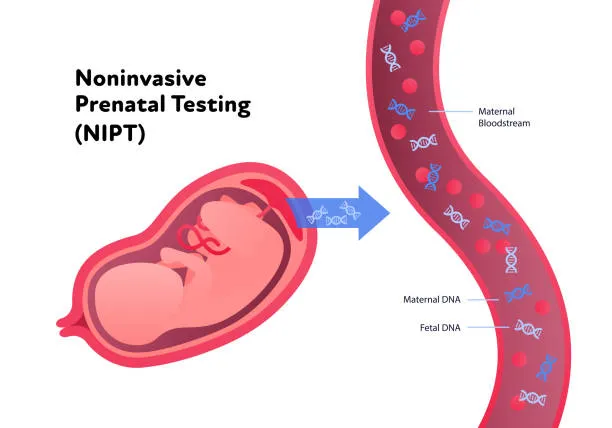
Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) is recommended by American professional societies such as the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM) for all pregnant women. NIPT, a blood test performed around 9-10 weeks of pregnancy, screens for fetal aneuploidies by analyzing cell-free DNA fragments from maternal circulation, which are sufficiently concentrated for detection at this stage.
Historical Context and Broadening Recommendations
Initially, NIPT was primarily used for women at high risk of having a fetus with trisomy 21, 18, or 13. However, comparative studies in the general obstetric population demonstrated significantly lower false positive rates for NIPT than other prenatal screening methods. Consequently, major obstetric societies now recommend NIPT for all pregnant women, irrespective of their risk status. This recommendation also includes women who have undergone in vitro fertilization (IVF) with preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A).
Why NIPT is Still Recommended Post-PGT-A
Women who have had a euploid embryo transfer are considered a lower-risk group for fetal aneuploidy, yet NIPT is still advised. There are important differences between PGT-A and NIPT that must be considered when interpreting results from these tests sequentially.
Understanding PGT-A
PGT-A samples 5-10 trophectoderm cells, assuming they represent the baby’s genotype. However, this is not always accurate, as different PGT assays can yield varying results. Many PGT assays lack validation through nonselection trials. Mosaic or segmental results often found in PGT-A may not be confirmed by prenatal diagnostic tests such as amniocentesis. Thus, there is a gap between the time of blastocyst biopsy and the subsequent prenatal screening at around 10 weeks of pregnancy, with unknown developments occurring in this period.
The Role of NIPT
NIPT analyzes DNA fragments released from the placenta into maternal circulation, which occur as cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast cells undergo fusion and apoptosis cycles. NIPT examines the ratio of maternal to placental cell-free DNA, known as the fetal fraction, which affects test sensitivity. NIPT utilizes either whole genome sequencing or targeted sequencing of specific chromosomes and has undergone multiple clinical validation studies.
The Value of Sequential Testing
The generalized use of NIPT means embryos created via IVF and PGT-A often undergo two rounds of testing: directly via PGT-A and then through NIPT screening. Although this might seem redundant, if NIPT detects an aneuploidy later confirmed by diagnostic testing (missed by PGT-A), this second screening is invaluable.
Study Findings on NIPT After PGT-A
Our recent publication in AJOG MFM investigated the positive predictive value (PPV) of NIPT in pregnancies conceived after IVF and PGT-A. We aimed to provide data for interpreting these tests when used sequentially. We identified 1,139 patients who underwent embryo transfer after PGT-A followed by first-trimester NIPT. Eight patients had abnormal NIPT results, but invasive diagnostic testing revealed only one abnormal karyotype: Turner mosaicism (45 X0 in 80% of cells), resulting in a PPV of just 12.5%, significantly lower than the general population’s 69%.
Implications for Clinicians and Patients
Clinicians and patients must recognize that those transferring a euploid embryo face a relatively lower risk of fetal aneuploidy than the general population, thus altering the NIPT’s PPV in this context. Despite this, our study supports recommending NIPT even for women who have undergone PGT-A. Physicians should counsel patients on the lower PPV to avoid unnecessary stress or anxiety over potential false positive findings.
In summary, while NIPT and PGT-A serve different roles in prenatal screening, both are crucial for providing a comprehensive assessment of fetal health, especially in IVF pregnancies.
#PGT-A #Non-invasive prenatal testing #Preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy #NIPT #fertilitycenter #ilababyIVFandSurrogacy #LGBTQ+ family planning #SurrogacyColombia #体外受精 #IVF #单身生育 #试管婴儿生育诊所 #哥伦比亚试管婴儿 #哥伦比亚代孕